
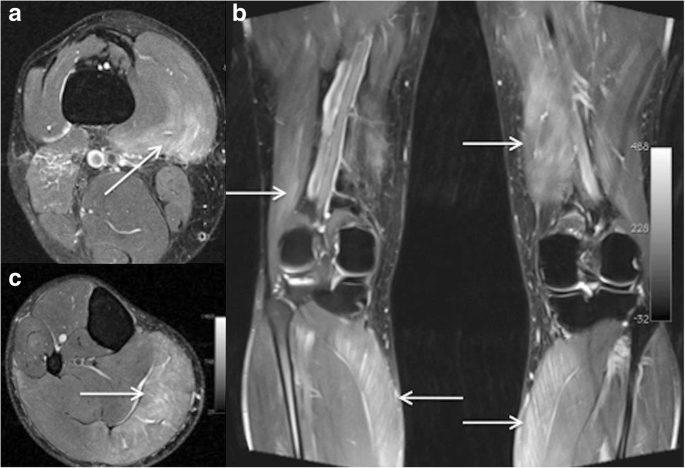
Brain and spinal cord - an MRI brain scan can look for brain tumours, possible causes of a headache, abnormal tissue growth and to assess damage after a stroke.Bones, joints and muscles - to help diagnose injuries or abnormalities affecting your joints, particularly your back, knee or hip and to detect conditions such as arthritis or tendon tears.Your doctor may recommend an MRI scan to examine different parts of your body including: Since this time, millions of patients worldwide have received gadolinium-based contrast agents before having an MRI scan. The most common MRI contrast agents contain gadolinium and have been in use since 1983. If your doctor recommends that you have an MRI scan with a contrast agent, the agent will usually be injected into a vein in your body.
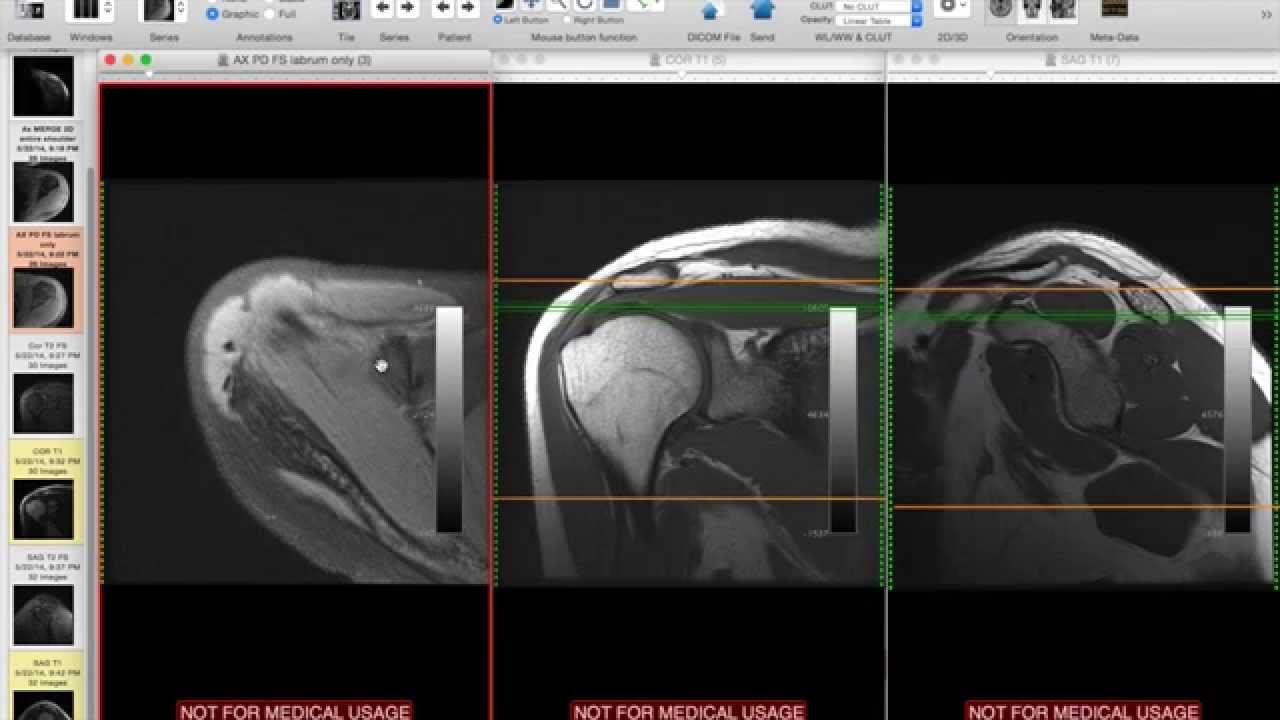
Doctors who specialise in analysing MRI scans are called radiologists.Īn MRI contrast agent is a special dye used to improve the visibility of certain tissues on an MRI scan. This means it can help diagnose, plan treatment for and monitor many different medical conditions.

It’s suitable for every part of the body, including bones, soft tissues (such as blood vessels, ligaments and muscles) and the brain. It does not use ionising radiation as X-rays do. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of scan that uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce very detailed two- and three-dimensional pictures of the inside of your body - in fact, the images produced are the most detailed of any type of scan available today.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
